
- #Vision loss normal lens normal retina how to#
- #Vision loss normal lens normal retina series#
- #Vision loss normal lens normal retina windows#
Special photographs help document the results. Just like how blood leaks from weak blood vessels, so does the dye. Within 45 seconds, the dye reaches the back of the eye. During the test, a dye is injected into your arm. While the retina is very thin, the test can measure retinal thickening as small as a thousandth of a millimeter.Ī fluorescein angiogram is a test that can detect diabetic retinopathy. Your doctor may perform an optical coherence tomography, which is a laser exam of the back of the eye. For signs of macular edema, the doctor looks at the macula in the back of your eye, but this may not be enough for a diagnosis. To detect retinopathy, the doctor looks at all the retinal tissues. With the use of special lenses and lights, the doctor will visually examine your retina. About 20 to 30 minutes later, your eyes will be fully dilated. The drops used may sting for a short time. The doctor will then dilate your pupils and examine the retina. People with many diabetes related problems with their vision can still wear contact lenses. Your ophthalmologist (eye doctor) will first check for any changes to your glasses or contact lens prescription. Managing your diabetes-by staying physically active, eating healthy and taking your medicine-can also help you prevent or delay vision loss. This is why it’s important for people with diabetes to have dilated eye exams at least once a year or more often if you have a problem.

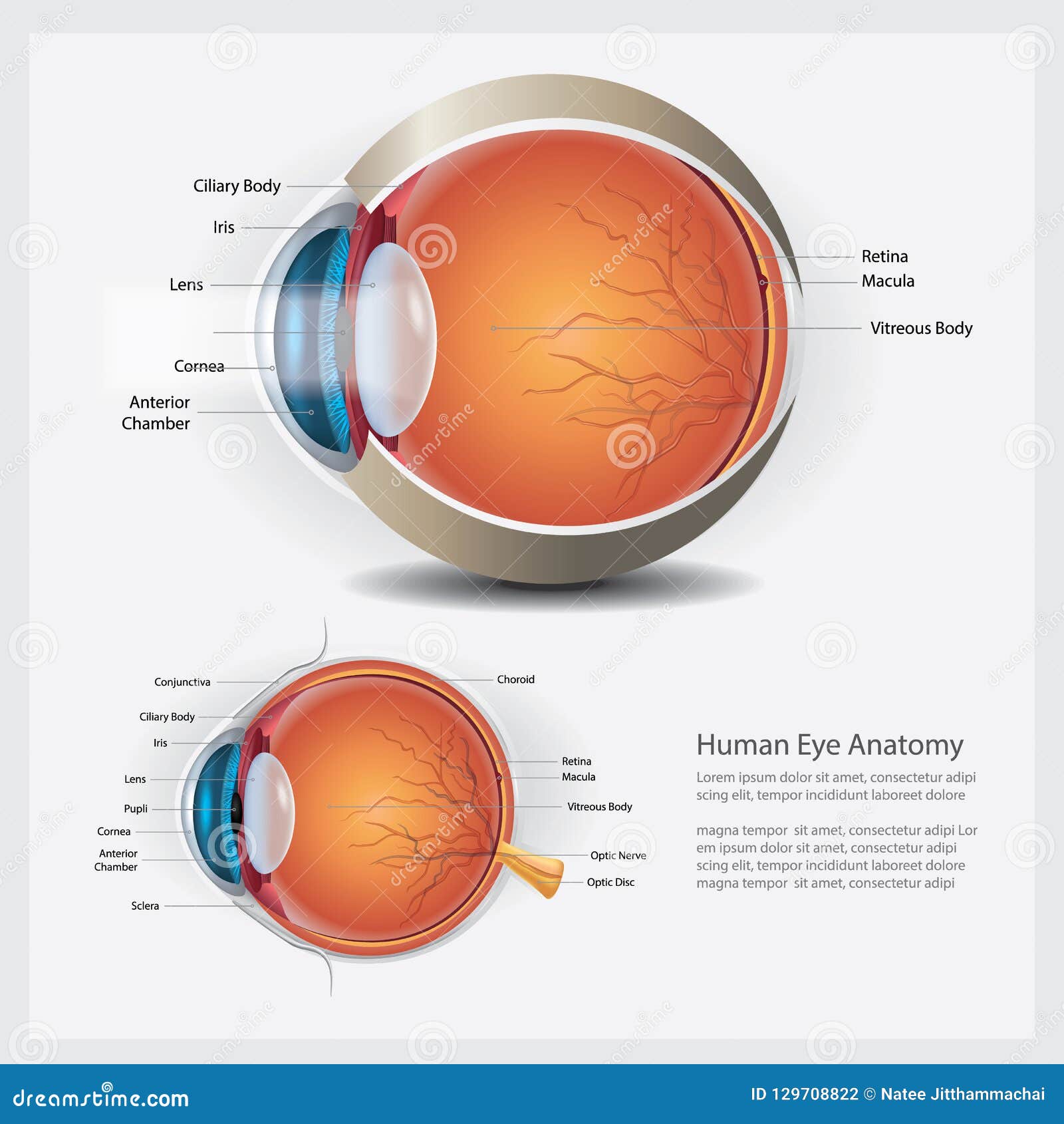
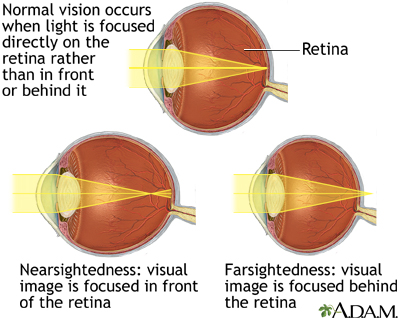
You can have 20/20 vision and still have diabetic retinopathy. This condition is known as retinal detachment, and it can happen suddenly or slowly over time. This leads to scar tissue, which can build up on the back wall of the eye and stretch the retina, eventually separating it from the back of the eye. These new blood vessels are weak and can easily break and bleed. When the new blood vessels form, it’s called proliferative retinopathy. Starving retinal tissue produces growth causing new blood vessels to form on the surface of the retina.
#Vision loss normal lens normal retina series#
In another process, blood vessels damaged by hyperglycemia (high blood sugar, or high blood glucose) close, and a series of events begin. The swelling associated with diabetes in the macula, the central part of the eye responsible for staring straight ahead, called diabetic macular edema. This causes the retina to thicken, creating blurred vision. Fluid leaks out of the blood vessels and into the retinal tissue which can cause vision problems. This is called non-proliferative retinopathy. The damage can cause the blood vessels to become leaky, like a water hose with holes in it.

The tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina can be damaged by diabetes. This wall contains a very thin piece of light-sensitive tissue: the retina. Light passes through the transparent front lenses, as if through the lenses of a camera, until it reaches the back wall of the eye. The structure of the eye is like a camera.
And if you already have diabetes-related eye disease, advances in treatment can save your sight. This is an important step since eye damage may have no symptoms at first. The good news: Advances in testing are catching problems before serious retinal changes occur. Diabetes can also make you more likely to have other eye conditions, including cataracts and glaucoma. Both are under the scope of diabetic eye disease, which includes all the retinal changes caused by diabetes. Two of the most common types of vision loss related to diabetes are macular edema and retinopathy.
#Vision loss normal lens normal retina windows#
The eyes may be windows to the soul, but for people with diabetes, looking deep into the retina can also reveal a diabetes-related eye disease.
#Vision loss normal lens normal retina how to#
How to detect and treat vision loss from diabetic eye disease


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
